Prototyping
Design and/or assembly project?
Think about Aluminium Foundry Prototypes
Aluminium Foundry Prototyping
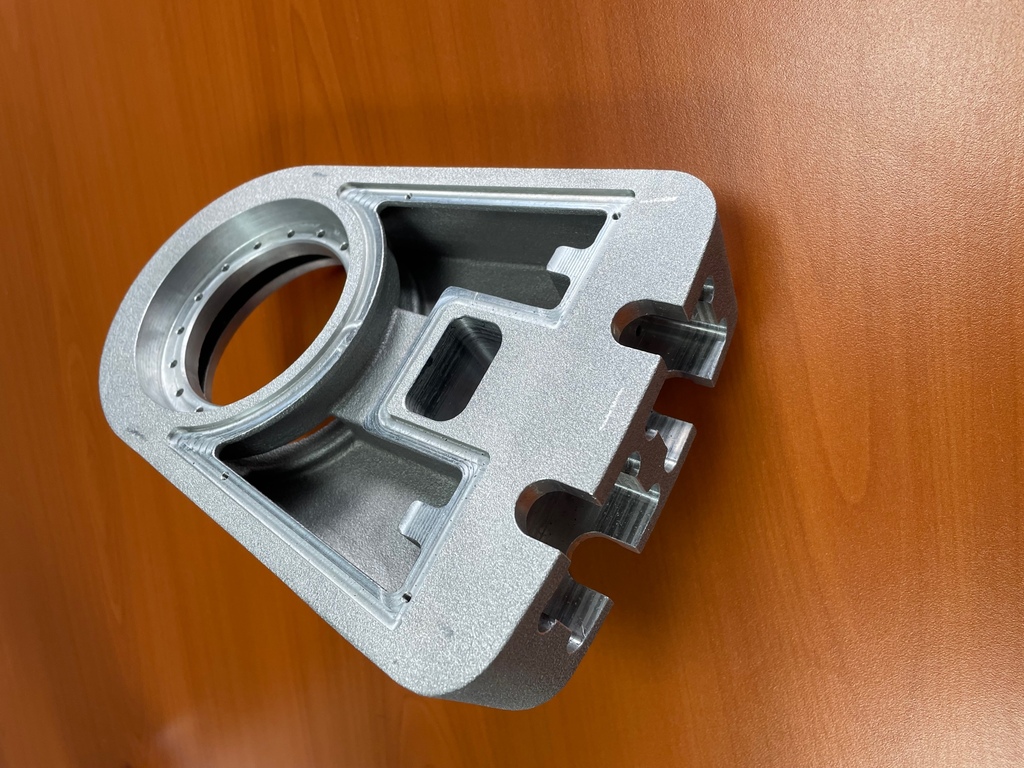
First of all, an aluminium casting prototype is an initial part produced as part of the product development process. Aluminium casting is a manufacturing process in which aluminium is melted in liquid form and then poured into a specially designed mould to create a solid part of the desired shape.

Bring Your Design and Assembly Projects to Life with Rapid Prototyping in Aluminium Foundry !
Here is a more detailed explanation of the process of creating Aluminium Cast Prototypes:
- First we design the prototype using a computer and computer-aided design (CAD) software. We then create a 3D model of the prototype, specifying the dimensions, shapes and characteristics of the final product.
- Next, we make a 3D-printed sand mould, which is adapted to the design of the prototype. This mould will serve as a negative for the finished product. It has to be precise and smooth to allow production of a prototype in an aluminium foundry.
- The aluminium is melted in a special furnace at high temperatures (the temperatures depend on the shapes and other parameters). Once the liquid aluminium has reached melting temperature, it is cleaned and prepared for casting into the prototype mould.
- We then proceed to casting, pouring the molten aluminium into the prepared mould. Gravity is used to fill the mould, allowing the liquid aluminium to take on the shape of the prototype.
- After casting, the aluminium begins to solidify. The cooling time can vary depending on the size and complexity of the prototype. Once the right temperature has been reached, the mould is broken to recover the aluminium prototype.
- Finally, the cast aluminium prototype is finished. This involves sawing, grinding, polishing or machining to achieve the desired precision and quality.
Prototypes are examples in aluminium that can be modified:
The cast aluminium prototype is then evaluated to ensure that it matches the design specifications. However, if adjustments are necessary, modifications can be made to the mould by redesigning (CAD) a new aluminium prototype, followed by a new casting cycle.
Advantages of Aluminium Prototypes :
Aluminium, a light but robust metal, lends itself perfectly to the combination of lightness and strength in the creation of prototypes, particularly for automotive parts, aeronautical components and sports equipment.
Aluminium excels as a conductor of heat and electricity, making it a preferred choice for creating prototypes of electrical, electronic and thermal components.
Aluminium is highly resistant to corrosion, making it durable and able to withstand environmental elements. This is particularly important for outdoor applications.
Casting in a sand mould, one of the foundry methods. It facilitates the production of the aluminium part, enabling complex prototypes to be created with great precision.
Aluminium prototypes have a high-quality surface finish, making them ideal for products that require a clean, aesthetic appearance.
Aluminium is an environmentally-friendly material because it is 100% recyclable. This metal helps to reduce the carbon footprint of prototype manufacture.
Heat sink: Because of its thermal conductivity, aluminium is often used as a heat sink in electronic prototypes to dissipate the heat produced by components.
Adaptability: Aluminium can be cast in a variety of shapes and sizes, and its alloys are versatile for a wide range of applications.
Durability: Aluminium prototypes have an extended lifespan. They are profitable in the long term.
Availability: Aluminium is widely available, making it easy to source alloys for prototype production.
Aluminium is the material of choice for your rapid prototyping projects:
In other words, whether it’s rapid prototyping for electronic components, sports equipment, cars or any other product, aluminium offers significant advantages in terms of lightness, strength and versatility. This makes it an attractive choice for many industries.
An aluminium blank is a must for your industrial projects.
Aluminium models thanks to Sable 3D printing
On the one hand, a cast aluminium prototype is often used to assess the feasibility of mass production of a product, testing its operation, durability and appearance. On the other hand, it is used to make changes to the design before going into series production. Ultimately it is used to verify the design and performance of a part or product, while providing a preview of its final appearance and functionality.